I. Introduction
Tick bites are a common occurrence for outdoor enthusiasts and people who enjoy spending time in nature. It is important to identify if a tick head is still in your skin because leaving it can lead to infections and other health complications. In this guide, we will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the symptoms to look out for, inspecting the affected area, using a magnifying glass, seeking medical attention, using a tick removal tool, irrigating the wound area, and preventing tick bites.
II. Symptoms to Look Out For
Most tick bites do not cause noticeable symptoms immediately, making it challenging to identify if the tick head is still in your skin. However, pain, swelling, and inflammation are common symptoms that could indicate the tick’s head is still in your skin. Some people may experience other symptoms, including fever, headache, muscle pain, and fatigue. It is important to remove the tick completely to avoid complications such as Lyme disease or other infections.
III. Inspect the Affected Area
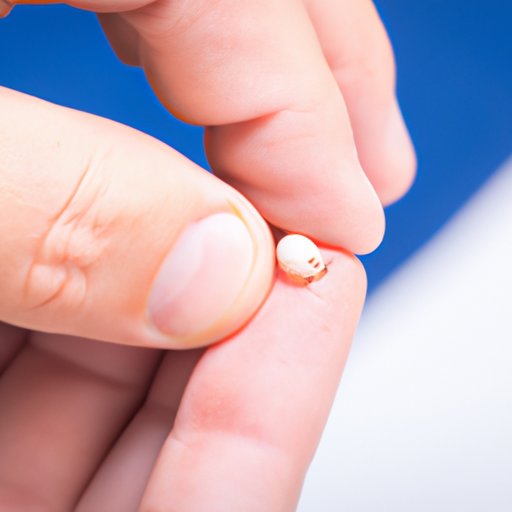
Inspecting the tick bite is crucial to ensure that the head of the tick is completely removed from your skin. Start by cleaning the area around the tick bite with soap and water. Use a mirror or ask a friend to check for signs of the tick’s head. Look for a small black dot that may resemble a splinter. If you cannot see it, feel the area with your fingers to check for any bumps or lumps.
Common mistakes to avoid when inspecting are squeezing or pinching the area and using oil or heat to remove the tick. These methods could cause the tick to release more saliva, increasing the risk of infections.
IV. Use a Magnifying Glass
A magnifying glass can be a helpful tool in accurately identifying if the tick’s head is still in your skin. It will allow you to get a closer look at the bite area, making it easier to spot any remnants of the tick. You can also use tweezers or a fine-tipped pair of scissors to remove any debris that may be obstructing your view.
Other tools that can be used to improve inspection accuracy include a flashlight, which can help identify the tick’s head in poor lighting conditions, and a camera, which allows you to take a picture of the affected area for closer examination.
V. Seeking Medical Attention
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect the tick’s head is still in your skin. A medical professional will have the tools and expertise to remove the tick safely and reduce the risk of complications. Medical professionals can clean the wound area thoroughly and prescribe antibiotics to reduce the risk of infections. Failure to seek medical attention can lead to severe health problems such as Lyme disease or Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
VI. Using a Tick Removal Tool
Tick removal tools are specialized devices designed to help you remove the tick’s head safely and effectively. These tools come in different shapes and sizes, including tweezers, tick hooks, and tick scoops. The most effective and recommended tool is the tick spoon, which is designed to scoop the tick’s head out of your skin.
When using a tick removal tool, it is crucial to work slowly and carefully to avoid leaving any remnants of the tick behind. Once the tick’s head is removed, place the tick in a sealed container and take it to a medical professional for identification and further testing if needed.
VII. Properly Irrigate the Wound Area
After removing the tick’s head from your skin, it is crucial to irrigate the wound area to prevent infections. You can use sterile saline solution or plain water to flush the wound and remove any dirt or debris that may have gotten into the wound. Avoid using rubbing alcohol or hydrogen peroxide, which can damage the skin and delay the healing process.
Specific products that can be used to irrigate the wound area include antibacterial ointments and wound cleansers, which help prevent infections and promote healing. Consult with a medical professional before using any products to ensure they are appropriate for your situation.
VIII. Prevention is Best
The best way to deal with tick bites is to avoid getting bitten in the first place. You can reduce your risk of getting bitten by wearing protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts and pants when venturing into wooded or grassy areas. Additionally, you can use insect repellent to keep ticks away.
Other measures you can take to prevent tick bites include keeping your lawn well-trimmed and removing any leaf litter or debris that could attract ticks. You can also apply tick-killing pesticides or seek professional pest control services for severe infestations.
IX. Conclusion
Tick bites can be a nuisance, but they can also pose serious health risks. It is crucial to identify if the tick’s head is still in your skin and remove it promptly to avoid complications. In this guide, we covered the symptoms to look out for, inspecting the affected area, using a magnifying glass, seeking medical attention, using a tick removal tool, irrigating the wound area, and preventing tick bites. If you suspect that the tick’s head is still in your skin, seek medical attention immediately.





